What is SGP Interlayer for Laminated Glass?
- What is SGP Interlayer?
- Superior Material Properties of SGP Interlayer
- SGP vs PVB: Core Comparison of Two Interlayers
- Why Choose SGP Interlayer?
- SGP Interlayer Performance in Glass Processing
- Key Considerations for Selecting and Purchasing SGP Interlayers
- Typical Applications of SGP Interlayer
- Pain Points and Solutions of SGP Interlayers
- Future Trends of SGP Interlayer
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about SGP Interlayers
- Conclusion: SGP Interlayer – The Core of the Future for High-Performance Laminated Glass
In contemporary architectural design, glass has long transcended its simple function of providing light, becoming a core material for structural and safety purposes. When discussing high-performance safety glass, we must delve into the heart of laminated glass – the interlayer.
Today, we'll focus on a game-changing "superstar" in the architectural glass industry: SGP interlayer.
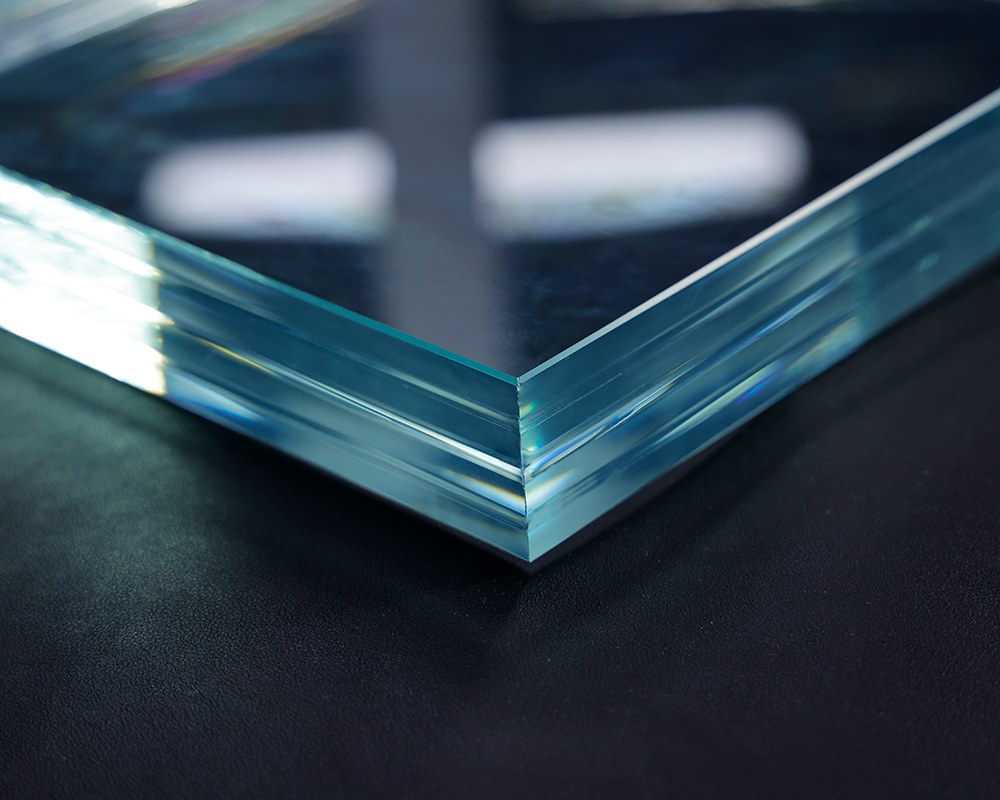
What is SGP Interlayer?
First, let's clarify a basic concept: what is SGP laminated glass?
Traditional laminated glass is a composite glass product consisting of two or more layers of glass sheets sandwiched with one or more layers of organic polymer interlayer, permanently bonded together under high temperature and pressure.
SGP, short for SentryGlas Plus, is an ion-exchange polymer interlayer developed by DuPont (now Kuraray).
SGP interlayer is also used in the manufacture of laminated glass, but it is not traditional PVB or EVA. SGP is a revolutionary material that endows laminated glass with unprecedented strength, stiffness, and durability. In short, SGP laminated glass is a structurally reinforced advanced glass that elevates the performance standards of safety glass to a whole new level.
Superior Material Properties of SGP Interlayer
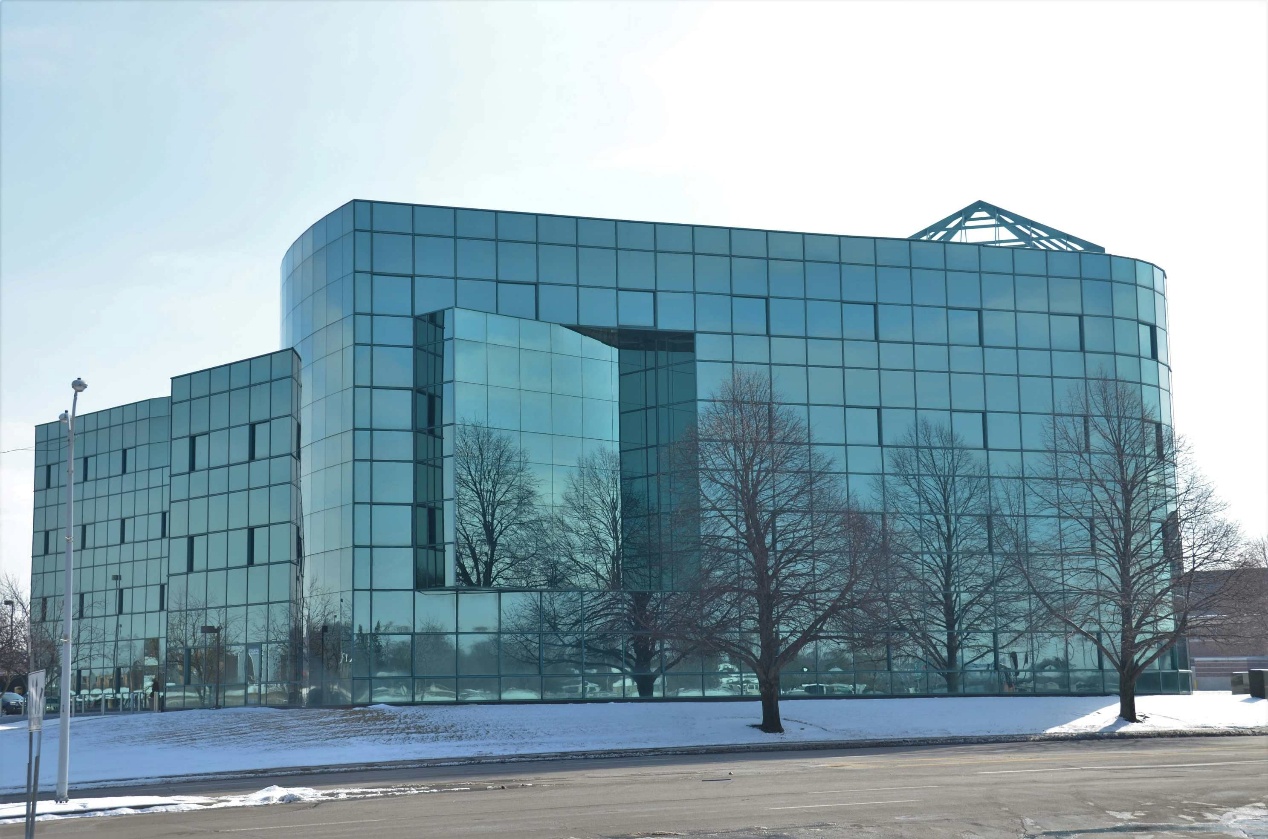

Superior architecture material- SGP Interlayer
SGP is called a "super interlayer" due to its unique ionomer structure. Unlike PVB's plasticized polyvinyl butyral, SGP's molecular structure gives it semi-rigid properties.
• Ultra-high strength and stiffness: SGP is 100 times stiffer than traditional PVB and has 5 times the tear strength. This means that, for the same glass thickness, laminated glass using SGP interlayer exhibits less bending deformation and greater load-bearing capacity.
• Excellent weather resistance: SGP is extremely resistant to moisture, high temperatures, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Unlike some interlayers, it does not easily fog or delaminate at the edges.
• Durable Optical Transparency: SGP boasts exceptionally high light transmittance and an extremely low Yellowness Index. Even after prolonged exposure to sunlight, it maintains crystal-clear transparency without yellowing.
• Stability in Extreme Climates: Whether in the humid heat of the tropics or the frigid temperatures of the Arctic, SGP interlayers maintain their mechanical properties and adhesive stability, making them ideal for high-performance glass.
SGP vs PVB: Core Comparison of Two Interlayers
In the field of laminated glass, the comparison between laminated glass PVB and SGP is a perennial topic. If you are selecting materials for your project, this comparison table will provide a clear overview.
Here we have prepared an English table for comparison in international projects:
Table 1: SGP Interlayer vs. PVB Interlayer Core Comparison
|
Feature |
SGP Interlayer (Ionoplast) |
PVB Interlayer (Polyvinyl Butyral) |
|
Stiffness & Rigidity |
Extremely High (Approx. 100x stiffer than PVB) |
Standard (Flexible) |
|
Tear Strength |
Very High (Approx. 5x stronger than PVB) |
Standard |
|
Post-Breakage Behavior |
High (Keeps glass intact, supports structure) |
Low (Glass fragments slump or fold) |
|
Weatherability (Moisture/UV) |
Excellent (Resistant to edge delamination) |
Good (Can be susceptible to moisture intrusion) |
|
Optical Clarity (Yellownes) |
Excellent (Ultra-clear, very low yellowness index) |
Good (Can have a slight yellowish tint) |
|
Structural Performance |
Can be used as a structural component |
Non-structural, primarily for safety/retention |
|
Cost |
Premium |
Economical |
Summary of Core Differences:
The biggest difference between laminated glass PVB and SGP lies in their behavior after breakage.
• When PVB laminated glass breaks, the glass fragments adhere to the film, but the overall structure becomes soft and droops, primarily serving a "splash-proof" function.
• After SGP interlayer glass breaks, thanks to its ultra-high stiffness and strength, the SGP film continues to "hold" the broken glass fragments and maintains considerable structural support, allowing it to still bear a certain load after breakage. This is known as "safety redundancy design."
Why Choose SGP Interlayer?
Choosing SGP laminated glass means you're choosing "active safety" rather than "passive safety."
• Safer Structural Support: SGP allows glass to transform from a passive safety component into an active structural load-bearing component. This is crucial in glass floors, glass staircases, frameless glass railings, and large glass panels.
• Durable Optical Aesthetics: The ultra-clear transparency and anti-yellowing properties of SGP interlayer make it the perfect partner for high-end commercial displays, museum windows, and ultra-clear glass curtain walls, ensuring the building's "lasting beauty."
• Ultimate Protection Against Extreme Weather: In areas prone to hurricanes and typhoons, SGP laminated glass is a recognized storm protection solution. It can withstand stronger wind pressure and the impact of wind-blown debris, far exceeding traditional laminated glass.
• Achieve Thinner and Lighter Designs: Due to the high strength of SGP, designers can use thinner glass configurations to achieve the same or even higher safety standards. This means lighter glass weight, smaller supporting structures, and lower overall construction costs. This is the appeal of advanced glass solutions.
SGP Interlayer Performance in Glass Processing
The superior performance of SGP also places higher demands on glass processing. It cannot simply replicate the PVB process.
Lamination Process: SGP glass lamination is primarily accomplished through an autoclave process. While non-autoclave methods have been explored, the autoclave is the most mature and reliable method to ensure perfect bonding between SGP and glass.
Key Parameter Control:
• Temperature: SGP has a narrower processing temperature window than PVB, requiring more precise control of heating and cooling profiles.
• Pressure: Sufficient and uniform pressure is required to expel air and achieve complete bonding.
• Humidity: SGP is extremely sensitive to moisture (before processing). Therefore, SGP interlayers must be assembled in a low-humidity cleanroom.
• Avoid Defects: Improper glass lamination processes (such as excessively high temperatures or rapid cooling) can lead to bubbles, delamination, or internal stress problems.
• Process Differences Compared to PVB/EVA: PVB is relatively "forgiving," while SGP is "demanding." SGP requires a higher level of technology and more sophisticated equipment, especially in the process control of the autoclave.
Key Considerations for Selecting and Purchasing SGP Interlayers
Choosing an SGP interlayer is not just about buying materials, but also about choosing a partner. A professional SGP interlayer supplier must meet the following stringent standards:
Material Quality and Certification
This is the cornerstone of selecting an SGP interlayer.
• International Certifications: Check whether the supplier can provide complete international certifications, such as EN (European Standard) and SGCC (American Safety Glass Certification Committee).
• Physical Property Data: Require detailed SGP interlayer quality test reports, including key data such as tensile strength, peel strength, haze, and yellowing index (YI).
Supply Stability & Lead Time: Large-scale construction projects have extremely stringent time requirements.
• Inventory and Delivery: A high-quality SGP interlayer supplier should have stable safety stock and global logistics capabilities to ensure rapid response to customer needs.
• Customization Capability: Does the supplier support customization of different thicknesses (e.g., 0.76mm, 0.89mm, 1.52mm, 2.28mm) and widths to accommodate large glass sheets?
Technical Support & Processing Guide: As mentioned earlier, SGP glass processing is quite complex.
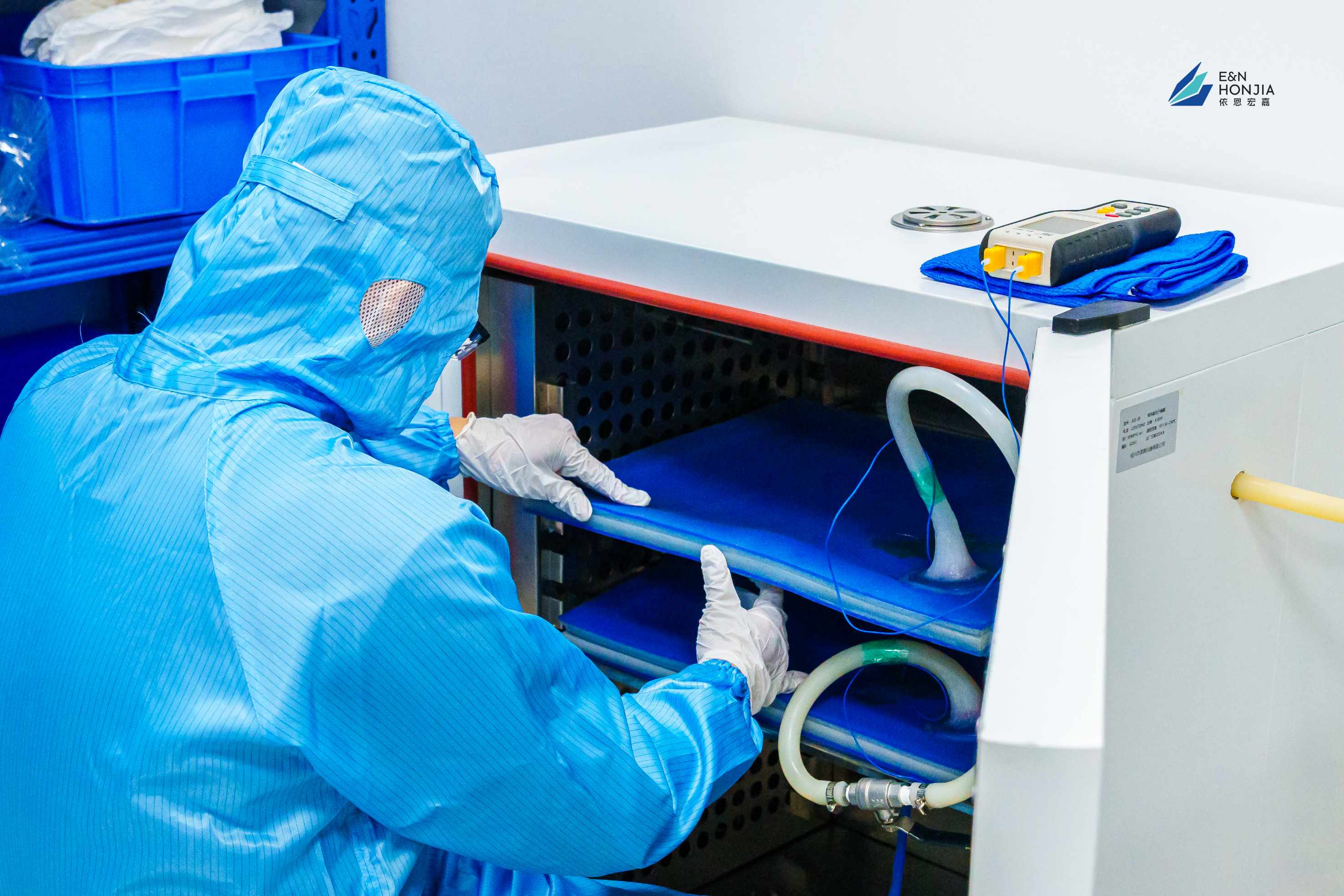

• Processing Guidance: Does the supplier provide detailed SGP glass lamination process guidance documents (including autoclave temperature, pressure, and time curves)?
• On-site Support: Is there an experienced technical team capable of assisting glass processing plants with the initial lamination test (Trial Run) and employee training?
Environment & Packaging: SGP is sensitive to environmental conditions, especially humidity.
• Vacuum Packaging: Must be sealed in high-barrier vacuum aluminum foil bags with an internal humidity indicator and desiccant.
• Environmental Regulations: Materials must comply with global environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH directives.
Reputation & Case Studies
• Project Experience: Verify if the supplier has a portfolio of landmark building projects worldwide.
• Client Base: Consider whether their typical clients include well-known architectural glass manufacturers, curtain wall processing plants, and structural glass engineering companies.
In summary: Choosing the right SGP interlayer depends on quality, certification, supplier capability, and glass processing experience.
• Customization Capabilities: Can the supplier support customization of different thicknesses (e.g., 0.76mm, 0.89mm, 1.52mm, 2.28mm) and widths to accommodate large glass sheets?
Typical Applications of SGP Interlayer
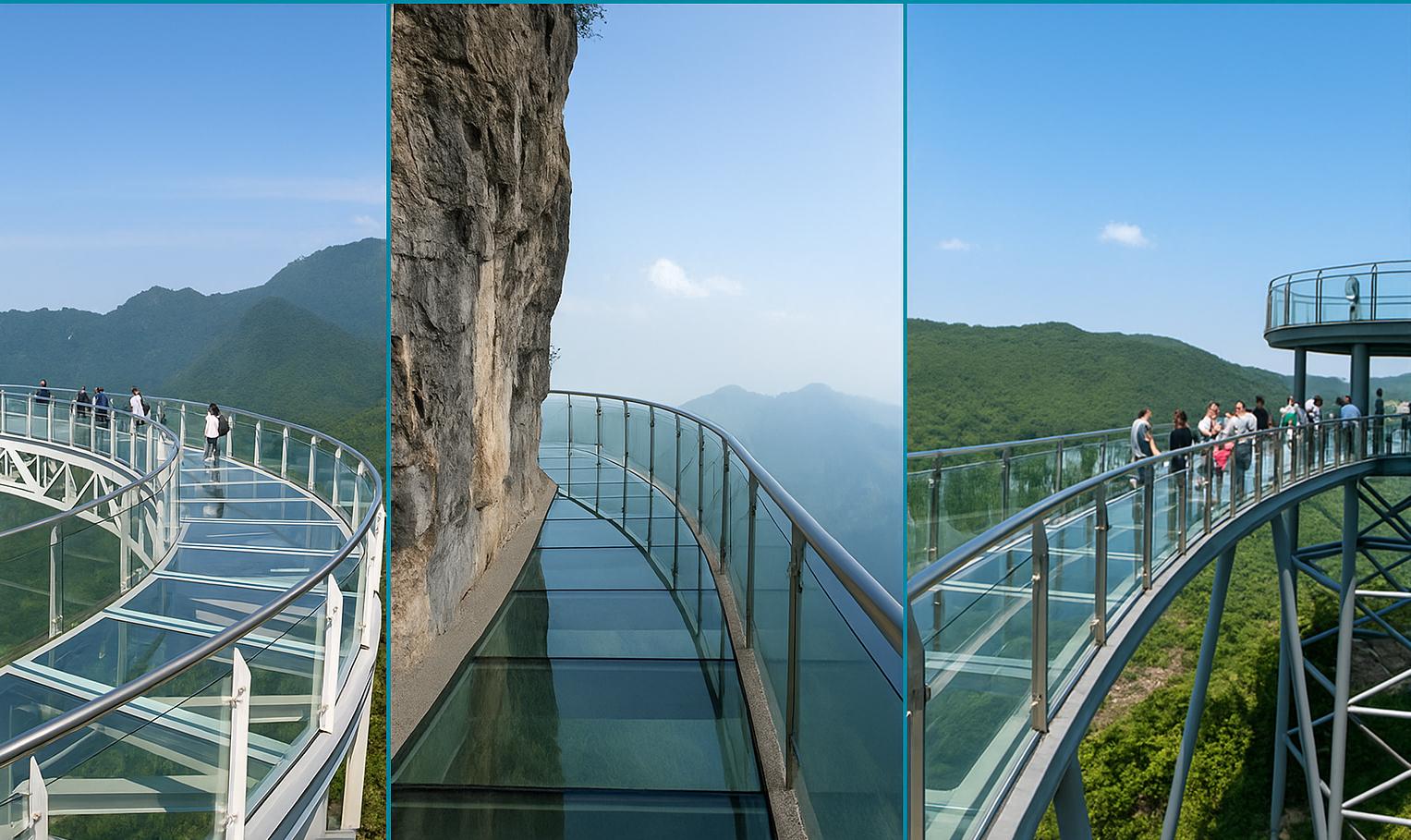

Applications of SGP Interlayer
The high added value of SGP interlayer makes it the preferred choice for high-end and specialty advanced laminated glass applications:
- Curtain Walls & Skylights: Especially in high-rise buildings and large-span skylights, SGP can withstand greater wind and snow loads.
- Frameless Balustrades & Facades: The high rigidity of SGP ensures that the balustrades remain upright even after the glass breaks, preventing falls.
- Glass Floors & Bridges: SGP provides the necessary structural redundancy and load-bearing capacity, making it a core safety material for popular glass walkways and observation decks.
- Blast & Bullet Resistant Glass: The high tear strength of SGP absorbs enormous impact energy, making it suitable for security in banks, embassies, and critical facilities.
- Hurricane-Resistant Glass: In coastal areas, SGP is the "gold standard" for protecting against extreme storm impacts.
Pain Points and Solutions of SGP Interlayers
Despite the superior performance of SGP, its widespread adoption also faces challenges.
Pain Points:
- High Cost: SGP raw material and processing costs are significantly higher than PVB.
- Strict Processing: Extremely high requirements are placed on temperature and humidity control (constant temperature and humidity) in the lamination room.
- High Difficulty: The glass lamination temperature window is narrow, easily leading to defective products.
- Solutions: To address the SGP interlayer problems, the industry has developed mature solutions.
Table 2: SGP Lamination Problems and Solutions
|
Problem |
Root Cause |
Solution |
|
High Cost |
Complex raw material (ionomer) and production. |
Optimize glass design (use thinner glass) to offset cost; Focus on life-cycle value, not initial price. |
|
Bubbles or Delamination |
Incorrect autoclave cycle (temp/pressure/time). |
Strictly follow the SGP interlayer supplier's recommended processing parameters. |
|
Moisture Contamination |
High humidity in the clean room or improper storage. |
Maintain a dedicated, climate-controlled clean room (low humidity); Use material immediately after opening. |
|
Processing Difficulty |
Lack of experience with ionoplast interlayers. |
Partner with an experienced SGP interlayer supplier that provides on-site technical training and support. |
Future Trends of SGP Interlayer
Innovation in SGP interlayers has never stopped, and advanced glass trends are unfolding around it:
Higher Performance: Developing lighter, stronger, and stiffer ionoplast interlayers to further push the limits of structural design.
Functional Composites: SGP will be increasingly combined with smart dimming films (PDLC, SPD) or other functional films to create multifunctional integrated advanced glass.
Sustainability: Researching the use of bio-based raw materials or recyclable materials to manufacture ionoplast interlayers, reducing the carbon footprint.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about SGP Interlayers
Q: What exactly is SGP laminated glass?
A: SGP laminated glass is a high-performance laminated glass. It uses SentryGlas Plus (SGP), an ionoplast interlayer. It is renowned for its strength, stiffness, and lasting transparency, far exceeding that of traditional laminated glass, making it an advanced glass.
Q: What is the core difference between PVB vs SGP for Laminated Glass
A: The core difference lies in stiffness and structural performance after breakage. SGP is approximately 100 times stiffer than PVB. This means:
PVB: After breakage, the PVB film is flexible, causing the glass to sag, primarily serving to prevent shards from flying.
SGP: The SGP interlayer maintains extremely high stiffness after breakage, firmly holding the broken glass pieces in place and continuing to provide temporary structural support, preventing collapse or falling.
Q: Can SGP interlayer be used for curved or bent glass?
A: Yes, it can. SGP interlayer can be used to manufacture curved (arched) laminated glass. However, this requires highly precise glass processing techniques, especially in hot bending and autoclave lamination, where the control over molds and temperature profiles is more demanding than with PVB.
Q: Is SGP suitable for outdoor applications?
A: Absolutely. SGP is arguably designed specifically for demanding outdoor applications. It exhibits exceptional resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures (high or low). Compared to PVB, SGP virtually eliminates the issues of edge delamination or noticeable yellowing after prolonged use.
Conclusion: SGP Interlayer – The Core of the Future for High-Performance Laminated Glass

High-Performance SGP Laminated Glass
From large-scale curtain walls to sophisticated frameless railings, SGP interlayer is redefining the possibilities of laminated glass.
It is more than just an interlayer material; it represents a high-end solution. SGP empowers architects and designers with the freedom to pursue more transparent, safer, and more challenging designs. Through its unparalleled structural performance, enduring aesthetics, and superior durability, SGP is raising the bar for safety and lifespan of structural glass worldwide.
If you're looking for an advanced glass solution that combines safety, aesthetics, and performance for your next landmark project, SGP interlayer is undoubtedly your most reliable choice. With over 20 years of experience in the laminated glass industry, E&N provides you with a leading manufacturer of SGP interlayer and SGP laminated glass solutions.
